In recent years there has been a lot of talk about Industry 4.0, its implications, the countless advantages, and above all the upheavals -or better the developments- that Italian industries will have to face in the coming years.
With this article, we want to explain in a clear and simple way the concept of industry 4.0, the possible future scenarios and above all what AgiLAB can represent in this context.
The definition of industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 represents the concept of applicating digital technologies to industrial automation. The main purpose is to arrive at smart production processes within a 4.0 factory in which everything is connected and regulated by systems that analyse large amounts of data to continuously optimise production processes and make them faster and above all flexible, practically based on real-time market demands. But that’s not all: in Industry 4.0 the machines also communicate with each other to diagnose their systems to schedule maintenance and prevent breakdowns, and therefore machine downtime.
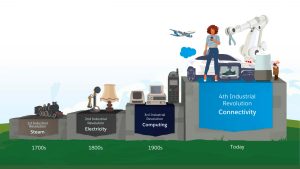
The number 4 recalls the concept of the 4th industrial revolution, that is starting in these years (it is not yet clear if and when it started). If the 1st industrial revolution (1700) was characterised by the use of steam engines and the 2nd by mass production through the use of assembly lines and electricity, the 3rd revolution industry (1970) saw the massive application of computers and industrial automation using robots.
And so, here we are at the 4th industrial revolution, which in reality it would be correct to call it more an Industrial Evolution since it involves the combined use of technologies already known, but never applied jointly.
Industry 4.0 and the labour market
Considering the future implications of Industry 4.0, one of the aspects on which attention is mostly focused is the labour market and what changes will Industry 4.0 bring on employment. According to a paper presented at the World Economic Forum 2016, some factors will negatively affect the employment level over the years, especially in the administration and production fields.
It is clear that in reality, the 4th industrial revolution will involve a change in the skills and abilities sought out. Industry 4.0 will require future workers with higher critical and creative abilities and problem-solving skills. It will be crucial for our country to reap the benefits of Smart Manufacturing from an employment perspective, thus providing workers with the digital skills necessary to carry out the tasks of the future.
Industry 4.0 and what changed within factories
The application of the concepts of Industry 4.0 to real production contexts leads to the definition of “smart factories” or factories in which the machines are completely connected and interconnected with each other and are able to readjust production in real-time, making it flexible and fast in accord to the requests of each individual customer. For a country like ours, founded on manufacturing, these aspects are crucial to face the challenges of global markets and to definitively exit the recession.
The robocentric interactive laboratory for experimenting with Industry 4.0
For many realities, all this is still science fiction and far from the real productive contexts.
So how is it possible to see a smart factory in the real world?
We can answer this question with one word: AgiLAB.
AgiLAB is the name given to the experimental interactive laboratory created by Eureka System; it emulates a scaled-down production process and allows you to experiment with the paradigms of digitised production.